5.2 The Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean (Central Limit Theorem)
Let’s start our foray into inference by focusing on the sample mean. Why are we so concerned with means? Two reasons: they give us a middle ground for comparison, and they are easy to calculate. In this section, we will see what we can deduce about the sampling distribution of the sample mean.
The Central Limit Theorem for a Sample Mean
The central limit theorem (CLT) is one of the most powerful and useful ideas in all of statistics. There are two alternative forms of the theorem, and both forms are concerned with drawing finite samples sizes, n, from a population with a known mean, μ, and a known standard deviation, σ. One of the forms says that, if we collect samples of size n with a “large enough” n, then the resulting distribution can be approximated by the normal distribution.
Applying the law of large numbers here, we could say that taking larger and larger samples from a population brings the mean, ![]() , of the sample closer and closer to μ. From the central limit theorem, we know that the sample means increasingly follow a normal distribution as n gets larger and larger. The larger n gets, the smaller the standard deviation gets. (Remember that the standard deviation for
, of the sample closer and closer to μ. From the central limit theorem, we know that the sample means increasingly follow a normal distribution as n gets larger and larger. The larger n gets, the smaller the standard deviation gets. (Remember that the standard deviation for ![]() is
is ![]() .) This means that the sample mean,
.) This means that the sample mean, ![]() , must be close to the population mean μ. We can say that μ is the value that the sample means approach as n gets larger. The central limit theorem illustrates the law of large numbers.
, must be close to the population mean μ. We can say that μ is the value that the sample means approach as n gets larger. The central limit theorem illustrates the law of large numbers.
The size of the sample, n, that is considered “large enough” depends on the original population from which the samples are drawn (the sample size should be at least 30, or the data should come from a normal distribution). If the original population is far from normal, then more observations are needed for the sample means or sums to be normal. Sampling is done with replacement.
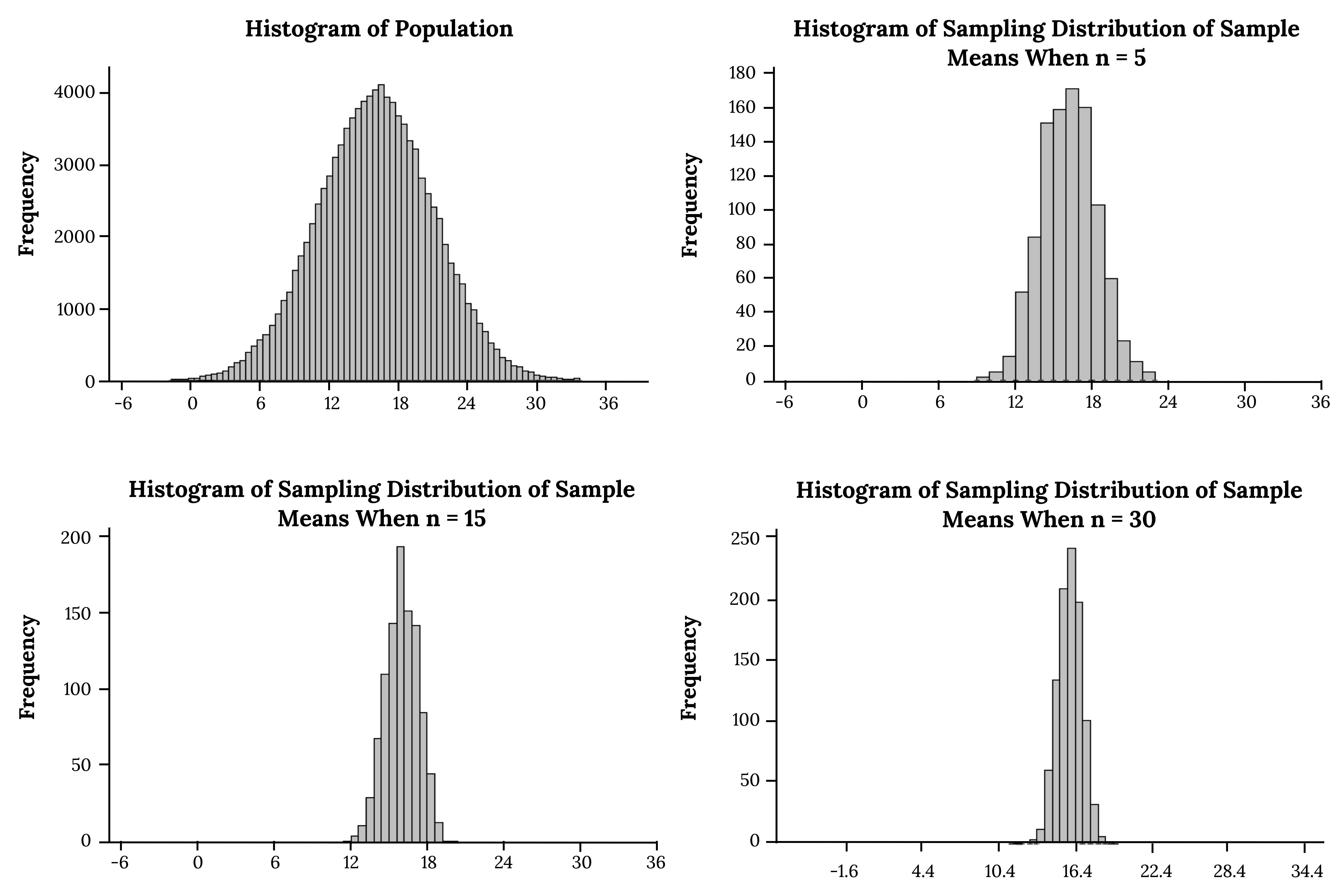
The following images look at sampling distributions of the sample mean built from taking 1,000 samples of different sample sizes from a normal population. What pattern do you notice?
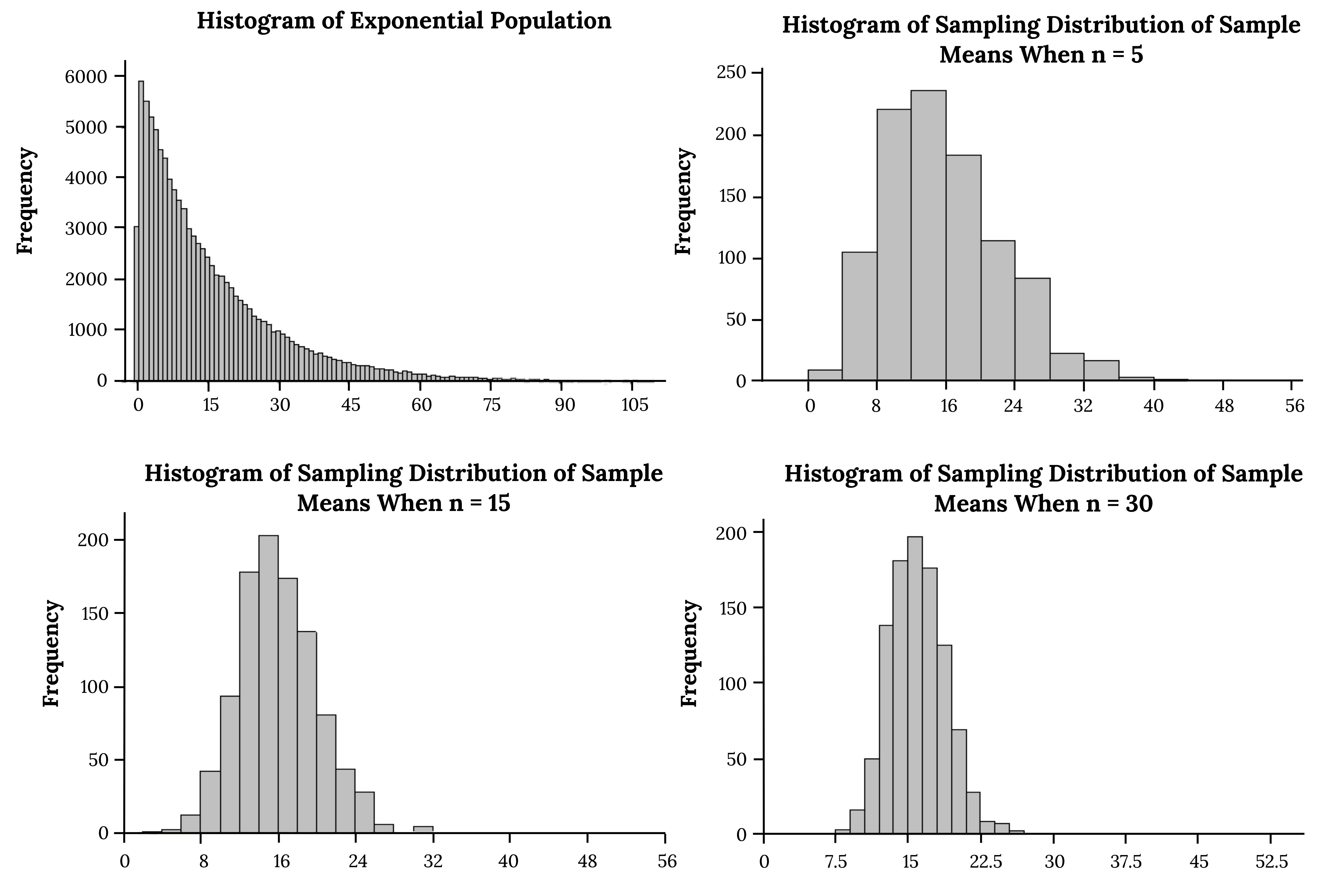
The following images look at sampling distributions of the sample mean built from taking 1,000 samples of different sample sizes from a non-normal population (in this case, it happens to be exponential). What pattern do you notice?
What differences do you notice when sampling from normal and non-normal populations?
Example
Suppose:
- eight students roll one fair die ten times
- seven roll two fair dice ten times
- nine roll five fair dice ten times
- 11 roll ten fair dice ten times
Each time a person rolls more than one die, he or she calculates the sample mean of the faces showing. For example, one person might roll five fair dice once and get 2, 2, 3, 4, 6.
The mean is ![]() = 3.4. The 3.4 is one mean when five fair dice are rolled. Suppose this person then rolls the five dice nine more times and calculates nine more means (for a total of ten means).
= 3.4. The 3.4 is one mean when five fair dice are rolled. Suppose this person then rolls the five dice nine more times and calculates nine more means (for a total of ten means).
As the number of dice rolled increases from one to two to five to ten, the following would happen:
- The mean of the sample means remains approximately the same.
- The spread of the sample means (i.e., the standard deviation of the sample means) gets smaller.
- The graph appears steeper and thinner.
We have just demonstrated the idea of central limit theorem (CLT) for means—as you increase the sample size, the sampling distribution of the sample mean tends toward a normal distribution.
To summarize, the central limit theorem for sample means says that, if you keep drawing larger and larger samples (such as rolling one, two, five, and finally, ten dice) and calculating their means, the sample means form their own normal distribution (the sampling distribution). The normal distribution has the same mean as the original distribution and a variance that equals the original variance divided by the sample size. Standard deviation is the square root of variance, so the standard deviation of the sampling distribution (a.k.a. standard error) is the standard deviation of the original distribution divided by the square root of n. The variable n is the number of values that are averaged together, not the number of times the experiment is done.
It would be difficult to overstate the importance of the central limit theorem in statistical theory. Knowing that data behaves in a predictable way—even if its distribution is not normal—is a powerful tool. We can simulate this idea using technology.
Suppose X is a random variable with a distribution that may be known or unknown (it can be any distribution). Using a subscript that matches the random variable, let:
- μX = the mean of X
- σX = the standard error of X
The standard deviation of ![]() is called the standard error of the mean and is written as:
is called the standard error of the mean and is written as:
![]()
Note here we are assuming we know the population standard deviation.
If you draw random samples of size n, then as n increases, the random variable ![]() which consists of sample means, tends to be normally distributed and the following is true:
which consists of sample means, tends to be normally distributed and the following is true:
![]() ~ N
~ N![]() .
.
To put it more formally, if you draw random samples of size n, the distribution of the random variable ![]() , which consists of sample means, is called the sampling distribution of the sample mean. The sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution as the sample size (n) increases.
, which consists of sample means, is called the sampling distribution of the sample mean. The sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution as the sample size (n) increases.
Using the CLT
It is important to understand when to use the central limit theorem. If you are being asked to find the probability of an individual value, do not use the CLT. Use the distribution of its random variable. However, if you are being asked to find the probability of the mean of a sample, then use the CLT for the mean.
The z-score associated with random variable ![]() differs from the score of a single observation. Remember, the mean
differs from the score of a single observation. Remember, the mean ![]() is the mean of one sample and μX is the average, or center, of both X (the original distribution) and
is the mean of one sample and μX is the average, or center, of both X (the original distribution) and ![]() .
.
![]()
We can take a familiar approach, using a z-table and standardizing, or we can use the technology of our choice.
Example
An unknown distribution has a mean of 90 and a standard deviation of 15. Samples of size n = 25 are drawn randomly from the population.
Find the probability that the sample mean is between 85 and 92. Let X represent one value from the original unknown population.
Solution
The standard error of the mean is ![]() =
= ![]() = 3. Recall that the standard error of the mean is a description of how far (on average) that the sample mean will be from the population mean in repeated simple random samples of size n.
= 3. Recall that the standard error of the mean is a description of how far (on average) that the sample mean will be from the population mean in repeated simple random samples of size n.
Let ![]() = the mean of a sample of size 25. Since μX = 90, σX = 15, and n = 25,
= the mean of a sample of size 25. Since μX = 90, σX = 15, and n = 25, ![]() ∼ N(90,
∼ N(90, ![]() ).
).
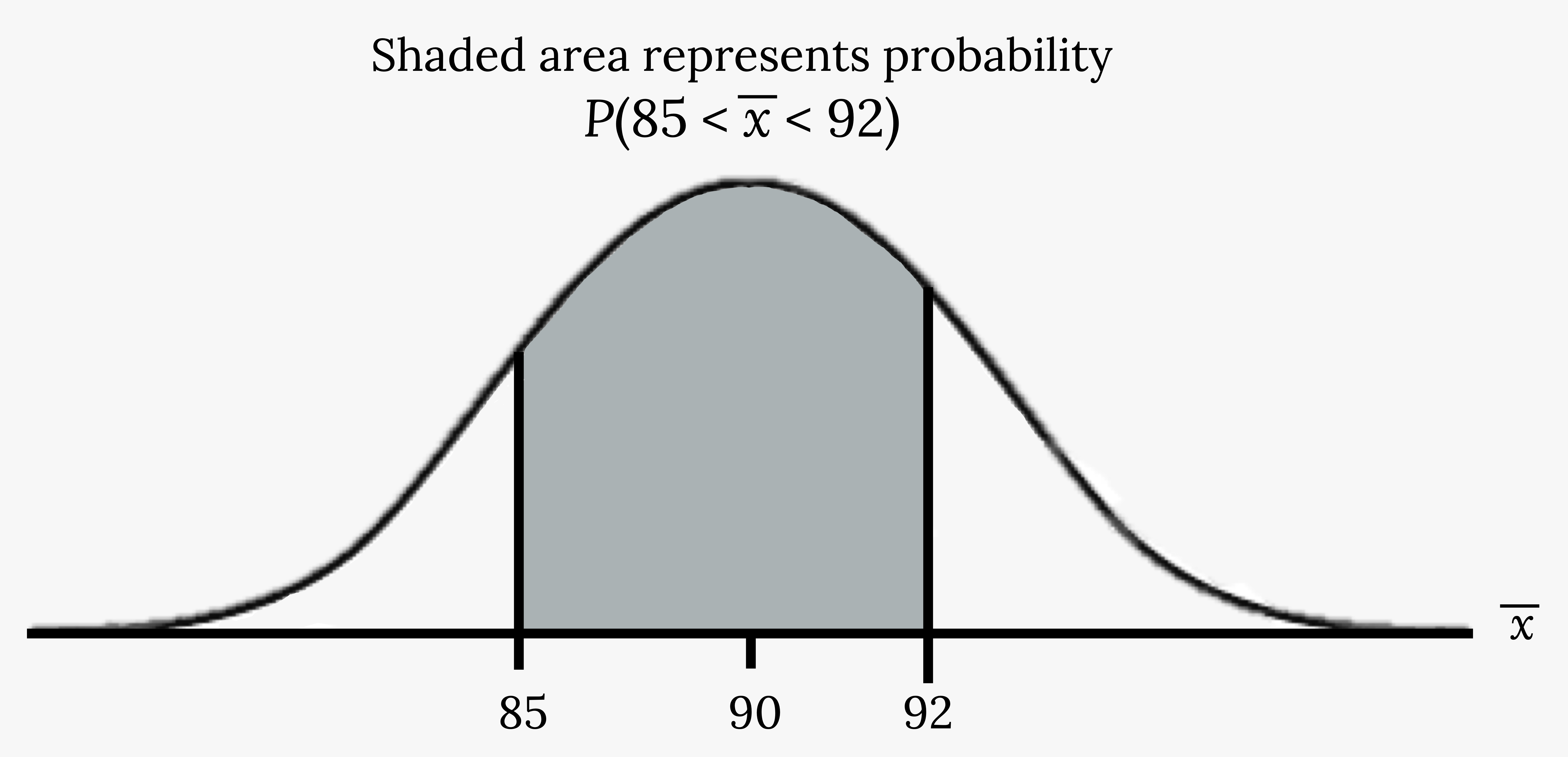
Find P(85 < ![]() < 92). Draw a graph.
< 92). Draw a graph.
Solution
This is a “between” problem. You will need to find two z scores, their corresponding probabilities, and then subtract.
Z1 = ![]() = -1.67
= -1.67
Z2 =![]() = 0.67
= 0.67
The probability that the sample mean is between 85 and 92 is 0.7475 – 0.0478 = 0.6997. Check this using technology.
Find the value that is two standard deviations above 90, the expected value of the sample mean.
Solution
To find the value that is two standard deviations above the expected value 90, use the formula value = μx + (#ofTSDEVs)(![]() )
)
Value = 90 + 2(![]() ) = 96
) = 96
The value that is two standard deviations above the expected value is 96.
Your Turn!
An unknown distribution has a mean of 45 and a standard deviation of eight. Samples of size n = 30 are drawn randomly from the population. Find the probability that the sample mean is between 42 and 50.
Additional Resources
Figure References
Figure 5.4: Kindred Grey (2021). Sampling distributions of the sample mean from a normal population. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Figure 5.5: Kindred Grey (2021). Sampling distributions of the sample mean from a non-normal population. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Figure 5.6: Kindred Grey (2020). Area under the curve. CC BY-SA 4.0. Adaptation of Figure 5.39 from OpenStax Introductory Statistics (2013) (CC BY 4.0). Retrieved from https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/5-practice
Figure Descriptions
Figure 5.4: Four histograms. Top left—Histogram of Population; Top right—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = five; Bottom left—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = 15; Bottom right—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = 30. All histograms follow typical bell-curve shape and as n increases, the shape gets more narrow around the mean.
Figure 5.5: Four histograms. Top left—Histogram of exponential population; Top right—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = five; Bottom left—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = 15; Bottom right—Histogram of Sampling Distribution of Sample Means when n = 30. All histograms are skewed right and as n increases, the plot gets more narrow around the mean.
Figure 5.6: Normal distribution curve where the peak of the curve coincides with the point 90 on the horizontal axis. The points 85 and 92 are labeled on the axis. Vertical lines are drawn from these points to the curve and the area between the lines is shaded. The shaded region represents the probability that 85 < x < 92.
If there is a population with mean μ and standard deviation σ, and you take sufficiently large random samples from the population, then the distribution of the sample means will be approximately normally distributed.

